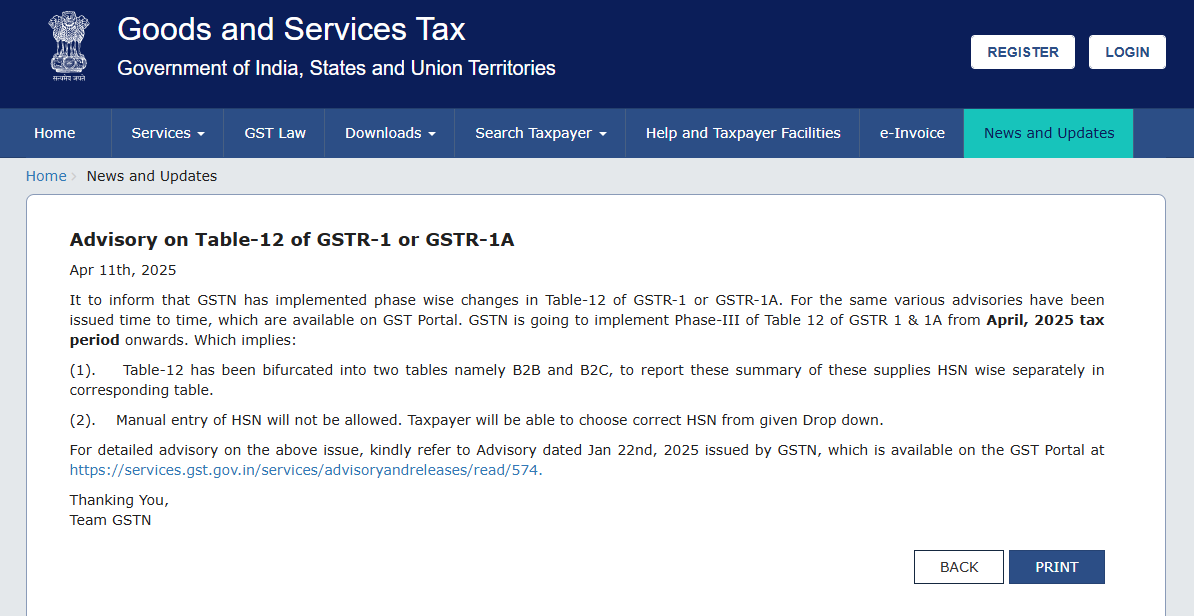
GSTN Rolls Out Phase 3 HSN Code Changes from April 2025

In a significant move to streamline and standardize tax reporting, the Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN) has announced the implementation of Phase-3 changes in Table-12 of GSTR-1 and GSTR-1A, effective from the April 2025 tax period. These changes focus on improving the accuracy of HSN code reporting and minimizing manual errors through automation and validation tools.
This is part of a larger phase-wise rollout, where GSTN has gradually introduced mandatory HSN code reporting since 2020. The latest phase is set to reshape how taxpayers—especially those involved in B2B and B2C transactions—report their supply data.
Phase-Wise Implementation: From Flexibility to Precision
Recap of Phase-2: Flexibility with Warnings
Implemented in November 2022, Phase-2 required taxpayers to mandatorily report HSN codes:
-
4-digit HSN for taxpayers with turnover up to ₹5 crore.
-
6-digit HSN for taxpayers with turnover above ₹5 crore.
While manual entry was allowed in Phase-2, the portal would issue warning alerts for incorrect or incomplete entries, but taxpayers could still proceed to file returns.
Phase-3: Key Changes Effective April 2025
With Phase-3, GSTN is shifting from flexible warnings to automated accuracy:
1. Table-12 Now Split Into B2B and B2C Tabs
-
Taxpayers must now report HSN summaries for B2B and B2C supplies separately.
-
This bifurcation ensures clearer classification and easier reconciliation for authorities and taxpayers alike.
2. Manual Entry of HSN Codes Disabled
-
Manual input of HSN codes is no longer permitted.
-
Taxpayers must select valid HSN/SAC codes from a drop-down list, ensuring standardization.
3. Auto-Population of HSN Descriptions
-
Upon selection, the official HSN description will now auto-populate in a dedicated field called “Description as per HSN Code”—removing ambiguity and mismatches.
4. Validation of Supply Values
The GST system will now cross-verify the values reported in Table-12 with those in other tables of GSTR-1:
-
For B2B supplies, data will be validated against tables like 4A, 4B, 6B, 6C, 8, 9A, 9B, 9C, 15, and 15A (where recipient is registered).
-
For B2C supplies, validation will cover tables like 5A, 6A, 7A, 7B, 8, 9A (Export/B2CL), 9B, 9C, 10, 15, and 15A (where recipient is unregistered).
-
Amendments will only consider differential values for validation checks.
-
For now, these validations are in warning mode, meaning mismatches will trigger alerts, but return filing won’t be blocked.
Additionally, if any B2B supply is reported elsewhere in GSTR-1, the B2B tab in Table-12 cannot be left blank.
GSTN Rolls Out Phase-3 of HSN Reporting in Table-12 of GSTR-1 and 1A From April 2025
User-Friendly Enhancements in Table-12
To make the filing process smoother, GSTN has added new features:
-
“Download HSN Codes List” button to get a complete Excel sheet of updated HSN/SAC codes with official descriptions.
-
Searchable “Product Name as in My Master” function to auto-fill HSN, UQC, and quantity fields—helping businesses maintain internal consistency. (Note: This is optional.)
Implications for Taxpayers
-
Higher Accuracy, Lower Errors: With dropdown selections and validations in place, discrepancies in HSN code reporting are expected to reduce significantly.
-
Improved Compliance for Businesses: The separation of B2B and B2C HSN reporting ensures better audit trails and compliance clarity.
-
Preparation Required: Businesses must review and update their HSN code masters, align systems for dropdown-based selection, and ensure teams are trained to navigate the new interface.
-
Early Adoption Advantage: Embracing these changes early will help taxpayers avoid future filing issues when validations are made mandatory (beyond warning mode).
The GSTN’s Phase-III rollout is a decisive step toward cleaner, consistent, and more traceable GST returns. While the transition demands some adjustments, the long-term benefits of transparency and automation are set to outweigh the compliance challenges. Businesses are advised to update their systems, train teams, and stay tuned for Phase-IV updates.
